What is iOS? Unveiled in 5 Minutes: Key Features & Uses
Despite being a staple in many pockets and purses, iOS, the operating system powering iPhones, often remains a mystery even to its regular users.
This article aims to demystify iOS, offering a comprehensive guide that illuminates its functionalities, history, and distinctions from iPadOS. Whether you're a seasoned iPhone enthusiast or a curious newcomer, this guide promises to enrich your understanding and appreciation of the intricate world of iOS.

What is Apple iOS?
Apple iOS stands for "iPhone Operating System." It's a specialized mobile operating system developed exclusively for Apple's hardware, such as the iPhone, iPad, and the now-discontinued iPod Touch. Imagine it as the brain behind your iPhone or iPad, orchestrating how the device operates and providing a foundation for various apps to function.
iOS: More Than Just for iPhones
While initially designed for the iPhone, iOS has expanded its reach. Originally launched as "iPhone OS" in 2007 alongside the first iPhone, it was later rebranded to "iOS" to reflect its broader compatibility with other Apple devices. The iPod Touch and iPad also ran on iOS until 2010 and 2019, respectively, when the iPad transitioned to a new, dedicated operating system called iPadOS.
iOS: A Blend of Technology
At its core, iOS is based on Apple's Macintosh OS X and supports programming languages such as Objective-C, C, C++, and Swift. This blend of technology provides a versatile and user-friendly interface, evident in actions like swiping across the screen to turn pages or pinching to zoom in and out.
The Evolution of iOS
iOS has evolved significantly since its inception. Major updates are released annually, with each bringing new features and improvements. As of September 2023, the latest version is iOS 18. This continuous development has made iOS a robust platform, supporting many applications and user interactions like tapping, swiping, and pinching.

iOS Devices: A Wide Range
What exactly are iOS devices? These are Apple's range of mobile devices that run on iOS. This includes the iPhone, which has been using iOS since its first model in 2007, and the iPod Touch, which adopted iOS the same year but was discontinued in mid-2022.
Android vs. iOS
In mobile operating systems, iOS is a prominent figure next to Android, its primary competitor. Android is known for its wide adoption due to its availability on devices across various price ranges, contrasting with Apple's typically higher-priced offerings.
How Does iOS Work?
The Role of iOS in Your Apple Devices
iOS is the powerhouse behind your iPhone or iPad, responsible for virtually every task you perform. It enables many activities, from making phone calls and sending text messages to capturing photos and videos. Additionally, iOS is the platform that runs popular apps like Facebook, TikTok, and Instagram, allowing you to download and use them. It also takes care of internet browsing, manages settings, and much more.

The Startup Process of an iOS Device
When you power up an iOS device, the operating system quickly springs into action, initializing the device. The first thing you encounter is the SpringBoard, iOS's main user interface. The SpringBoard showcases the icons of all installed apps, providing an easy and intuitive way to launch them.
Resource and Hardware Management
iOS goes beyond just a user interface; the brain manages the device's resources, including RAM, memory and storage. It also controls the hardware components like the camera and touchscreen, ensuring they work harmoniously with the software.
Communication and Services
A crucial aspect of iOS is its ability to offer various services. For instance, it facilitates push notifications, allowing apps to send you alerts and updates. This functionality is essential for apps to communicate with each other and the internet, making your experience seamless and integrated.
Built-in Apps and the App Store
iOS has a built-in app suite designed to enhance your user experience. These include Safari for web browsing, Mail for email handling, and Maps for navigation. What's more, iOS features the App Store, a digital marketplace where you can download and purchase a wide range of apps, games, and other digital content. The App Store is a pivotal element of iOS, providing access to a universe of applications that extend the capabilities of your device.
In summary, iOS is a multifaceted operating system that makes your Apple device function and enriches your experience with many features and applications.
Security and Privacy Features of Apple iOS
Apple's iOS is renowned for its robust security and privacy features, ensuring that your data and device are protected from various threats. Here's an overview of some key security aspects of iOS.
Apple ID and Biometric Authentication
Apple ID Support: One of the fundamental elements of iOS security is the Apple ID. It lets users securely sign into websites and apps using their existing Apple ID credentials. Furthermore, iOS supports advanced biometric authentication methods like Face ID and Touch ID, adding an extra layer of security.
Two-Factor Authentication: To bolster the security of Apple ID, iOS incorporates two-factor authentication. This feature adds a verification step, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access to your account.
Enhanced Privacy Controls and Secure Boot Chain
Fine-Grained Privacy Controls: iOS allows you to exercise precise control over your privacy settings. You can restrict apps from accessing your location information or receiving AirDrop content from unknown sources. iOS also empowers you to control whether apps can use Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, ensuring your permission is required for such access.
Secure Boot Chain: An essential security feature of iOS is its secure boot chain. This process ensures that only trusted and digitally signed code is executed during the device's boot-up. This mechanism is crucial for verifying the integrity of the code running on your device, safeguarding against unauthorized software and potential vulnerabilities.
Secure Enclave: A Hardware-Based Security Feature
The Secure Enclave is a significant hardware-based security feature integrated into iOS devices. It securely stores cryptographic keys in an isolated area, safeguarding them from potential compromises. The importance of Secure Enclave extends beyond iOS devices; it's also a critical security component in Apple TV, Apple Watch, Mac computers, and other Apple products.
Additional Security and Privacy Features

Data Encryption: All data on iOS devices is encrypted by default, providing robust protection for your personal information, messages, and photos.
App Store Security: The App Store's stringent review process ensures that apps are safe and adhere to privacy standards, protecting users from malware and security threats.
Privacy Labels and App Tracking Transparency: iOS offers data usage transparency through the App Store's privacy labels and empowers users with the App Tracking Transparency feature to control their data more effectively.
Regular Security Updates: Frequent iOS updates address security vulnerabilities and introduce new security features, maintaining the security integrity of the device.
Advanced Network Security: Features like private Wi-Fi addresses in iOS enhance privacy when connecting to public networks.
Source Verification for Messages and Calls: iOS identifies potentially fraudulent calls and messages using intelligent analysis and third-party apps for enhanced call screening.
In summary, combining biometric authentication and hardware-based security features like Secure Enclave, data encryption, privacy controls, and regular updates makes iOS a highly secure and privacy-conscious mobile operating system. These comprehensive features demonstrate Apple's commitment to protecting users' privacy and security.
Apple iOS Version History
Over the years, iOS has evolved significantly, introducing new features and enhancements with each version.
As of now, the latest version of iOS is iOS 18.2. This iteration continues Apple's tradition of annual updates, each bringing new functionalities and security improvements.
Exploring the Full List of iOS Versions
For those interested in delving deeper into the rich history of iOS updates, Apple provides a comprehensive list named Apple Security Updates and Rapid Security Responses.
How to Check Your iOS Version
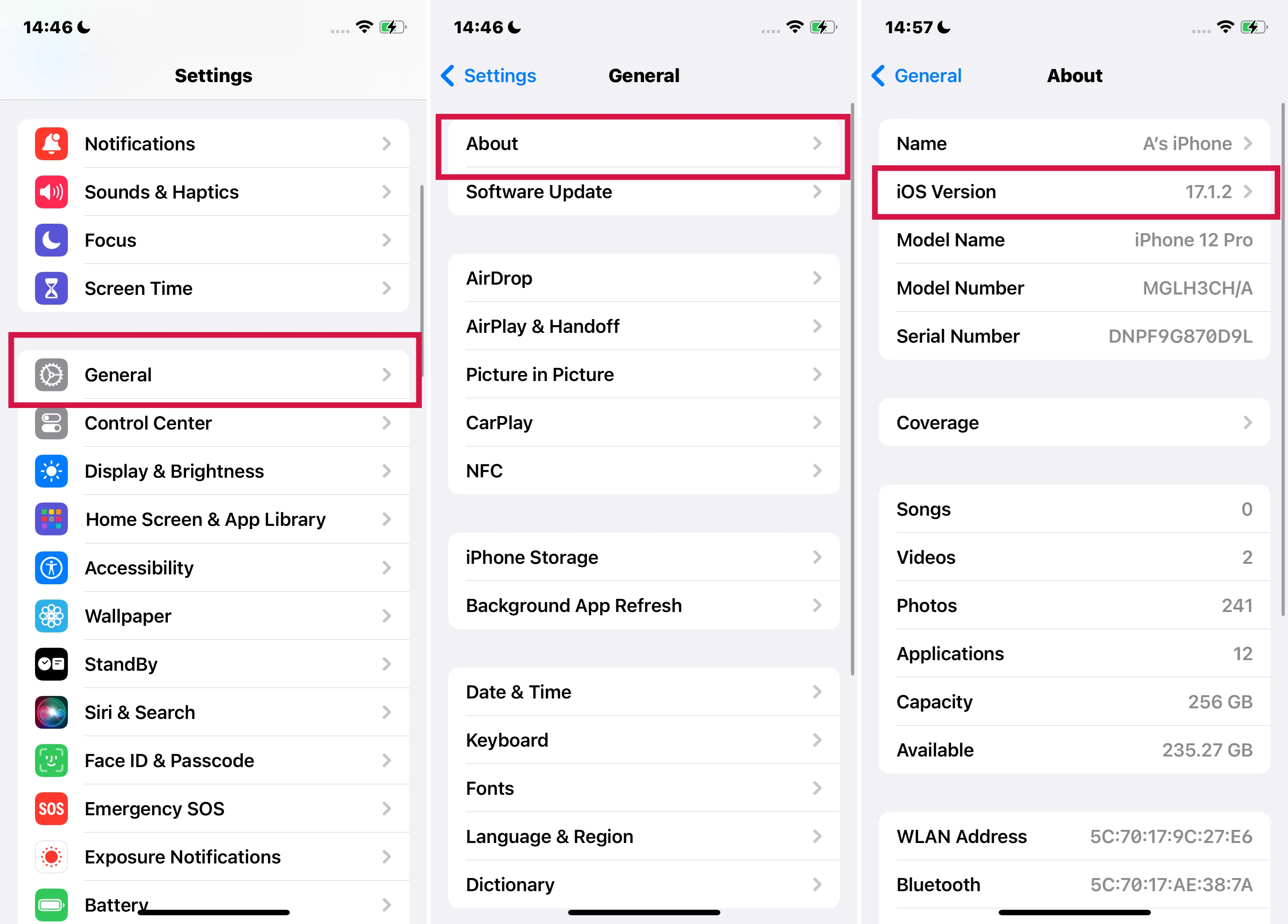
Are you wondering which version of iOS your iPhone or iPad is currently running? It's quite simple to find out. Just follow these straightforward steps:
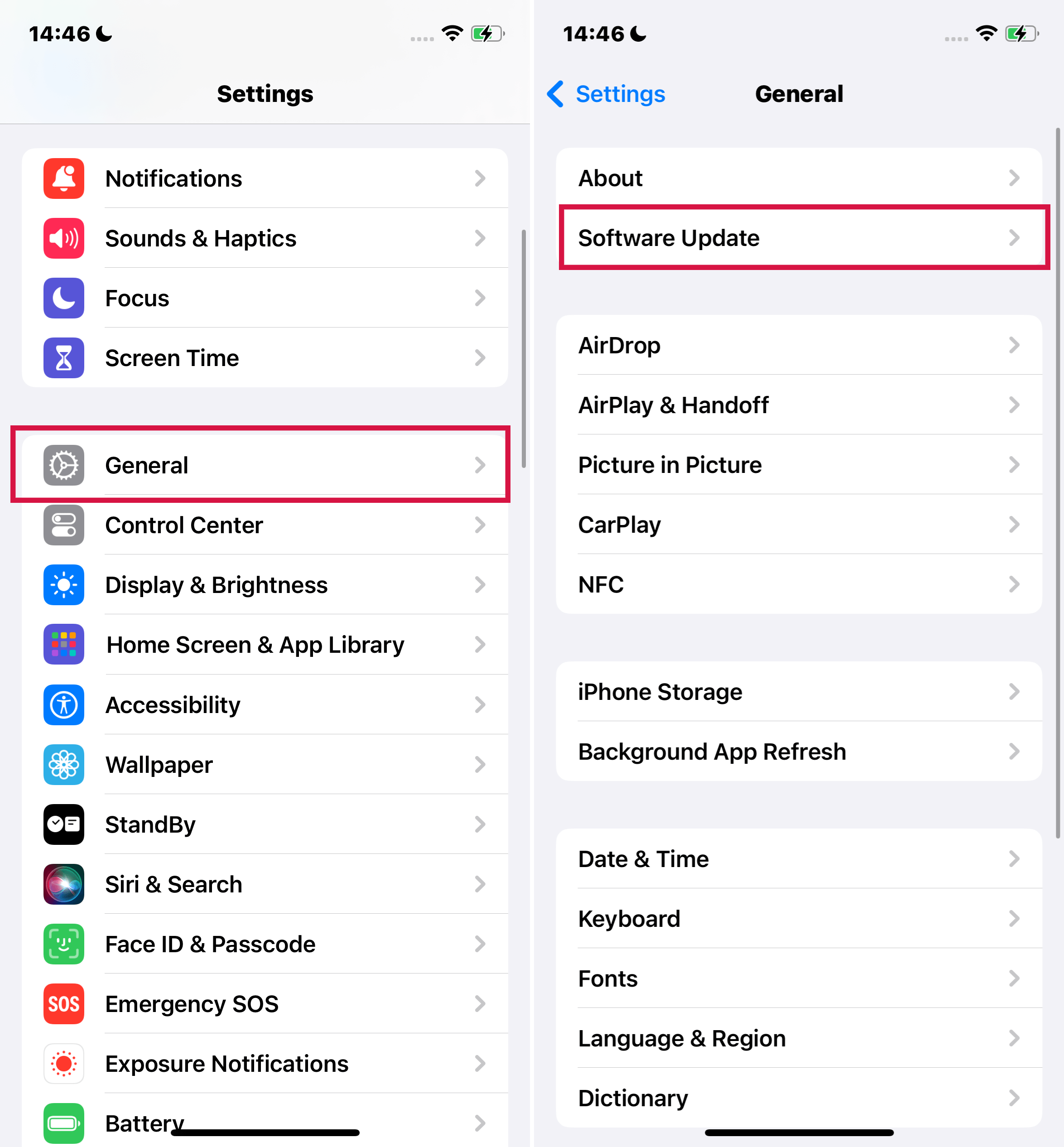
Begin by tapping on the "Settings" app icon on your device. This app allows you to adjust all settings related to your iPhone or iPad.
Once in the Settings menu, look for the option labeled "General" and tap on it. This section contains various device settings and information.
In the General settings, you'll find an option titled "About." Tap on this to access detailed information about your device.
Scroll until you find the "Software Version" field. The number next to this field indicates the current iOS version installed on your device.
If, upon checking your iOS version, you find that it's not the latest one, you can easily update your iPhone or iPad to the most current version.
To do this, go to "Settings," then "General."
Select "Software Update." If an update is available, you'll see an option to download and install it.
Can You Downgrade Your iOS Version?
Downgrading to a previous version of iOS is generally not supported by Apple. Once you update your iPhone or iPad to a newer version of iOS, Apple typically stops signing the older versions. This means you can't officially reinstall an older version of iOS once a newer version has been installed and authenticated on your device.
There are unofficial methods to downgrade iOS, often used by developers and tech enthusiasts, but they come with significant risks. These methods can lead to data loss, reduced device functionality, and potential security vulnerabilities. Additionally, using unofficial methods to downgrade iOS can void your warranty and may make your device ineligible for future support from Apple.
It's always recommended to back up your device before installing any updates, so if you encounter issues with a new version of iOS, you can at least restore your data from the backup. However, the actual iOS version will remain the updated one. For most users, the best practice is to stay updated with the latest official version of iOS to ensure optimal performance, security, and access to the newest features.
iPadOS vs iOS: Understanding the Key Differences

The distinction between iOS and iPadOS can be understood as two variations of the same operating system, each specifically tailored for different types of hardware: smartphones and tablets, respectively. Here's a breakdown of the key differences:
1. Multitasking and Extensibility
Multitasking: iPadOS excels in multitasking capabilities. Unlike iOS for the iPhone, iPadOS supports true multitasking modes, allowing apps to be displayed in split-screen mode or using features like Stage Manager to run multiple applications simultaneously.
External Displays and Accessories:
iOS for the iPhone is not designed to work with external displays in the same way as iPadOS.
Additionally, while iPhones can support mouse or trackpad input via AssistiveTouch, they do not natively support this feature, nor does Apple build keyboard or mouse accessories for the iPhone.
In contrast, the iPad is compatible with Apple's Magic Keyboard case and other accessories designed to enhance productivity.
2. Specific Feature Support
Sidecar, Apple Pencil, and Dock Interface: iOS for the iPhone lacks support for Sidecar external display mode, native desktop web browsing, Apple Pencil stylus, and the macOS-style dock interface, all of which are features available on iPadOS.
Apple Watch Compatibility: iPadOS does not support integration with the Apple Watch, which requires an iPhone for setup and basic functionality.

Telephony and Messaging
The iPad is not designed as a standalone telephony device. Its support for phone calls and messaging (iMessage or SMS) relies on a connected iPhone. An iPad cannot function as a standalone cellular phone for receiving calls.
Application Support and SDK Requirements
While iPadOS can run most iPhone-designed apps in a compatibility mode, these apps may not always function or display optimally if they're not properly optimized. Conversely, the iPhone cannot run iPadOS apps.
Due to different interface requirements and compatibility standards, developers must use specific SDKs for each platform - the iOS SDK for iPhone apps- and the iPadOS SDK for iPad apps.
In summary, while iOS and iPadOS share a common foundation, they are differentiated by their specific features and capabilities. They are designed to optimize the user experience on their respective devices - smartphones for iOS and tablets for iPadOS. This includes differences in multitasking abilities, accessory support, and application compatibility, reflecting the unique use cases and hardware specifications of iPhones and iPads.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, understanding the nuances of iOS and its evolution, including its version history, security features, and differences with iPadOS, provides valuable insights into Apple's operating systems.
Whether you're a long-time Apple user or new to the ecosystem, this knowledge enhances your experience and ensures you make the most out of your Apple devices.
Thanks for reading!

